Understand Window Energy Ratings: U-Value, Low-E Glass & SHGC
What makes energy-efficient windows genuinely efficient? It’s essential to know about U-value, low-E glass, and SHGC. These parts help determine how well a window saves energy. Knowing these ratings helps people pick the best home or building windows.
Window performance ratings are key to knowing how energy-efficient a window is. By looking at these ratings, people can find windows that save energy and help the planet. Learning about window energy ratings is the first step to choosing the right windows.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding window energy ratings is key for picking energy-efficient windows
- U-value, low-E glass, and SHGC are important for window energy ratings
- Window performance ratings affect a window’s energy efficiency
- Energy-efficient windows can save energy and reduce heat transfer
- Knowing about window energy ratings helps make smart window choices
- Window energy ratings are vital for understanding a window’s environmental impact
Understanding Window Energy Ratings: A Complete Guide
Window energy ratings are key to a building’s energy efficiency. They help homeowners and builders choose the right windows. The u-factor measures heat transfer, while the SHGC shows solar radiation entry.
Energy Star windows meet EPA energy standards. They have good u-factors and shock. Choosing these windows can cut energy use and bills. Other ratings include air leakage and condensation resistance.
What Are Window Energy Ratings?
Window energy ratings measure a window’s efficiency. They look at the u-factor, SHGC, and air leakage. This helps homeowners pick the best windows for their homes.
Why Energy Ratings Matter
Energy ratings help lower energy use and bills. They also make homes more comfortable and valuable, and they’re good for the environment.
Key Components of Window Energy Ratings
The main parts of window energy ratings are the u-factor, SHGC, and air leakage. These help homeowners compare different windows and choose wisely.
The Science Behind U-Value in Windows
The U-value is a key measure of a window’s thermal performance. It indicates how easily heat passes through the glass and frame. The lower the U-value, the better the insulation—meaning less heat escapes during winter or enters during summer. This directly translates into greater indoor comfort and reduced energy costs. The calculation considers every part of the window system: the type and number of glass panes, insulating gases between panes, the frame material, and the quality of seals and spacers.
How U-Value Works
-
Thermal Transmittance: The U-value, also called the heat transfer coefficient, quantifies how much heat is lost or gained through a window or building element.
-
Measurement Units: It is expressed as watts per square meter per Kelvin (W/m²K). For example, a window with a U-value of 1.4 will allow 1.4 watts of heat to move through each square meter for every degree of temperature difference inside versus outside.
-
Insulation Link: Lower U-values signify stronger insulation and higher energy efficiency, while higher values mean more heat loss and weaker performance.
Factors That Affect U-Value
-
Glass Panes: Multi-pane windows, especially those filled with inert gases such as argon or krypton, insulate far better than single-pane options.
-
Frame Material: Different frame materials conduct heat at different rates. Vinyl or fiberglass frames insulate better than aluminum, which naturally has high thermal conductivity.
-
Spacer Bars & Seals: The components that separate and seal the glass panes influence how much heat escapes at the edges of the window.
-
Low-E Coatings: Special low-emissivity coatings reflect heat back into the room or outward, reducing overall heat transfer.
Why U-Value Matters
-
Energy Efficiency: Windows with low U-values reduce the workload on heating and cooling systems, helping cut down energy consumption.
-
Indoor Comfort: Better insulation prevents cold spots, drafts, and overheating, keeping rooms comfortable throughout the year.
-
Environmental Impact: Selecting windows with strong insulating performance lowers household energy use, contributing to reduced carbon emissions.
Low-E Glass Technology: Advanced Window Solutions
Low-E glass is designed to make your home more energy-efficient without sacrificing natural light. Its nearly invisible coating reflects heat and blocks UV rays, keeping interiors cooler in summer and warmer in winter.
By reducing energy use and protecting your furnishings from fading, Low-E glass not only cuts utility costs but also enhances comfort and boosts your property’s value. It’s a simple upgrade with long-term benefits.
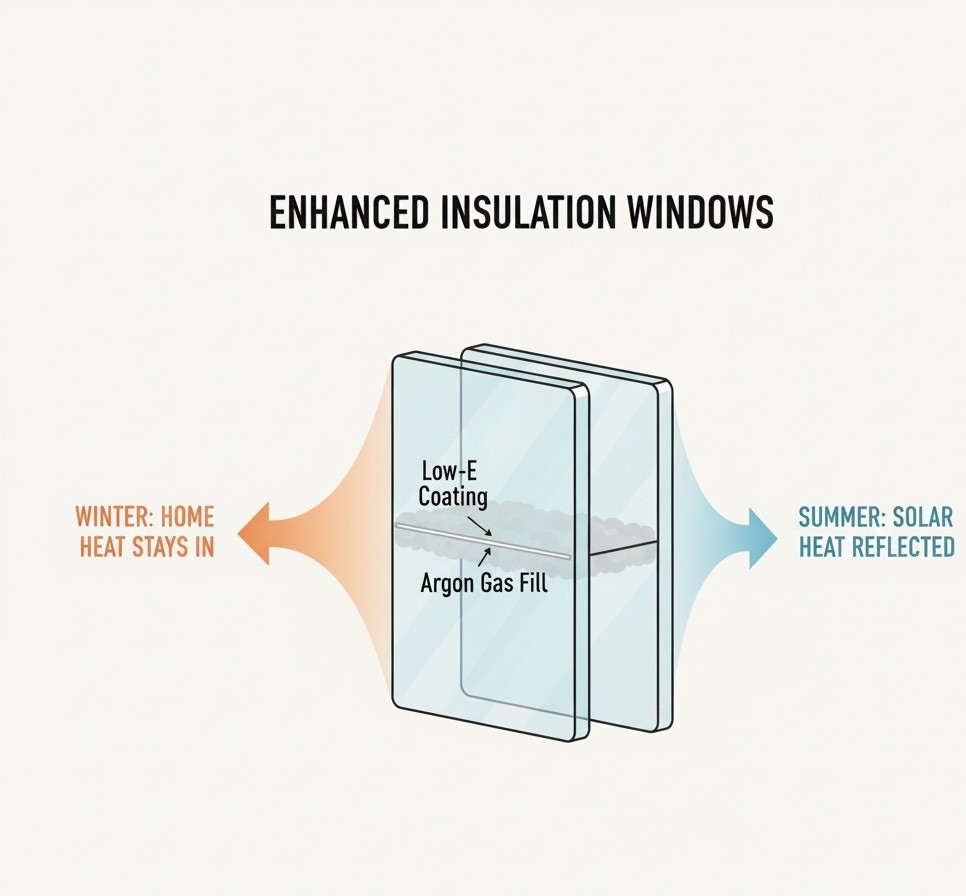
How Low-E Glass Works
Low-E (low-emissivity) glass functions through a specialized coating that modifies the way heat and light interact with the glass surface. The process involves:
-
Coating Application: A microscopically thin, transparent metallic oxide layer is deposited onto the glass during manufacturing.
-
Infrared Control: This coating reflects long-wave infrared radiation, which is responsible for heat transfer. As a result, indoor heat is kept inside during winter, while solar heat is reflected away in summer.
-
UV Filtering: The coating blocks a substantial portion of ultraviolet radiation, reducing the amount of harmful UV light that passes through.
-
Light Transmission: Unlike tinted or reflective glass, Low-E glass still permits high levels of visible light, ensuring natural daylight enters the building without distortion.
-
Selective Surface Placement: Depending on climate needs, the coating can be placed on different glass surfaces within a double- or triple-pane unit to optimize insulation and solar control.
-
Multi-Layer Interaction: In advanced types, multiple Low-E layers are used to fine-tune performance, balancing solar gain, insulation, and clarity.
Benefits of Low-E Glass Coatings
Low-E glass is more than just an upgrade—it’s a smarter way to improve comfort, efficiency, and sustainability at home or in commercial spaces. Its advanced coating technology delivers multiple advantages:
-
Energy Efficiency: By slowing heat transfer, Low-E glass reduces dependence on heating and cooling systems, cutting energy costs.
-
Consistent Comfort: It helps maintain balanced indoor temperatures year-round, eliminating cold drafts in winter and excess heat in summer.
-
UV Protection: The specialized coating blocks harmful ultraviolet rays, safeguarding furniture, flooring, and artwork from fading or damage.
-
Added Value: Energy-smart windows enhance a property’s market appeal, making them a reliable long-term investment.
-
Eco-Friendly Impact: With lower energy demand, Low-E glass supports greener living and contributes to more sustainable buildings.
Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) Explained
The Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) is key for energy-efficient windows. It shows how well a window blocks sun heat. Lower SHGC means better performance.
Windows with low SHGC, like those with low SHGC glass, save energy and keep homes cooler in summer.
ER-rated windows consider U-value, SHGC, and more. This gives a full view of a window’s energy use. Choosing windows with low SHGC and U-values makes your home more comfortable and saves energy.
- Reduced energy consumption and lower energy bills
- Minimized heat gain during the summer months
- Improved comfort and reduced glare
- Increased durability and extended window lifespan
Knowing about SHGC helps homeowners pick the right windows. Whether you want low SHGC glass, er-rated windows, or low U-value windows, many choices fit your needs and budget.
Energy Star Certification and Window Ratings
Energy Star certification is a sign of top-notch energy-efficient windows. These windows must have a low U-value glass and a good SHGC value. The Energy Star program helps people choose the best energy-saving products, like windows.
The Energy Star certification checks how well a window saves energy. It looks at how well the window stops heat, keeps air in, and blocks UV rays. Windows with a low e rating saves more energy and reduces bills.
Energy Star Requirements
Windows must meet certain energy standards to get the Energy Star label. These standards change depending on where you live, so it’s important to pick windows that fit your area’s needs. Look at the window’s U-value, SHGC value, and air leakage rate.
Climate Zone Considerations
Where you live affects how well windows save energy. For example, warm places need windows with a low SHGC value to keep cool, and cold places need windows with a low U-value to stay warm. Choosing the right windows for your climate helps save energy and money.
Certification Process
The certification process tests a window’s energy-saving abilities. It checks how well the window stops heat, keeps air in, and blocks UV rays. You know you’re getting the best energy-saving windows by picking Energy Star-certified windows.
Choosing the Right Windows Based on Energy Ratings
Energy ratings are key when picking windows. The window energy rating u value shows how well a window keeps heat. Choosing a window with a low u-value helps save energy and money.
Window glass energy ratings matter, too. They examine solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) and Energy Star certification. This helps homeowners pick windows that save energy and money in the long run.
Climate Considerations
Climate affects window choice. A low u-value window is vital in cold places to keep warmth in. In hot areas, a high SHGC window helps lower cooling costs.
Budget Planning
It’s important to consider your budget when picking impact windows. Low-value windows might cost more at first, but save money later. It’s good to balance costs and benefits.
Long-term Energy Savings
Choosing the right windows can save energy and money over time. Windows with low U-values and high Energy Star ratings cut down on bills, leading to big savings and a greener home.
Also Read,
Aluminum in Architectural History: A Captivating Rundown
5 Practices That Can Damage Your uPVC Doors
All You Need to Know About Thermal Windows
Essential DIY Tips for UPVC Sliding Doors Repairs
Thermally Broken Aluminum Doors and Windows: Yay or Nay?
The What, Why, and How of French Doors
Conclusion: Making an Informed Window Selection
When you think about getting new windows, knowing about energy ratings is key. The U-factor, SHGC, and Energy Star labels are essential. They help make your home use less energy and save money over time.
Choosing windows with low SHGC and U-factor ratings keeps your home cozy and reduces bills. Also, picking windows right for your area’s weather is smart. It makes your home fit better with the local climate.
Getting energy-saving windows is a smart move for the future. It means lower bills and a greener home. Take your time to figure out what you need. Then, pick windows that help you save energy.
FAQ
What is a window’s U-Factor?
The U-factor measures how well a window prevents heat from escaping or entering. The lower the U-factor, the better the insulation, which helps improve energy efficiency and comfort in your home.
-
Indicates heat transfer through the window
-
Lower value = better insulation performance
-
Key rating for colder climates where heat retention matters
What is SHGC (Solar Heat Gain Coefficient)?
The SHGC tells you how much solar radiation passes through a window. A low SHGC blocks more sun heat, which helps keep interiors cooler in warm climates.
-
Measures how much solar heat enters through the glass
-
Scale ranges from 0 to 1 (lower values mean less heat gain)
-
Important factor for sunny, hot regions
What is the difference between U-Factor and R-Value?
While both measure insulation, they work in opposite ways. U-factor shows how much heat is lost, while R-value shows how resistant a material is to heat transfer.
-
U-factor = rate of heat transfer (lower is better)
-
R-value = resistance to heat transfer (higher is better)
-
Both help determine overall energy efficiency
What is an Energy Star–certified window?
Energy Star windows meet strict efficiency standards set by the U.S. government. They’re designed to lower energy use while maintaining comfort, using certified U-factor and SHGC ratings.
-
Must meet regional U-factor and SHGC requirements
-
Backed by government testing and certification
-
Proven to reduce energy bills and improve comfort
How do I choose the right window energy ratings for my climate?
The best window depends on your local weather conditions. Cold regions need insulation (low U-factor), while hot climates need solar control (low SHGC).
-
Cold climates → focus on low U-factor for insulation
-
Warm climates → choose low SHGC for solar control
-
Moderate climates → balance both ratings
-
Use Energy Star climate-zone guidelines for accuracy
What is the difference between a double-pane and a triple-pane window?
The difference lies in the number of glass layers. Double-pane windows have two sheets of glass, while triple-pane adds an extra layer for greater insulation—but usually at a higher cost.
-
Double-pane → two glass layers, good efficiency, lower cost
-
Triple-pane → three glass layers, higher insulation, more expensive
-
Extra pane improves soundproofing and energy performance
How do Low-E coatings improve window energy efficiency?
Low-E coatings are ultra-thin, transparent layers that control how heat and UV rays interact with the glass. They improve efficiency without reducing natural light.
-
Reflect infrared heat (keeps warmth in during winter, out during summer)
-
Block harmful UV rays that cause fading
-
Allow visible light to pass through for natural brightness





